In today’s fast-moving world, stress has become an inevitable part of daily life. Whether stemming from work demands, relationship challenges, or financial concerns, stress can negatively impact both our mental and physical health. A key hormone involved in how our bodies respond to stress is cortisol. Learning about cortisol and its effects is important for recognizing signs of elevated stress and finding effective ways to manage it. Let’s explore what cortisol is, the difference between acute and chronic stress, and highlight eight common symptoms of high cortisol levels. With this understanding, we can take steps to reduce cortisol and better manage stress.
Cortisol is a hormone produced by the adrenal glands, which sit atop the kidneys. Often called the “stress hormone,” cortisol is released in response to stress and helps regulate many vital functions, including metabolism, blood pressure, and immune system activity. In short bursts, cortisol is beneficial, enabling us to respond effectively to immediate stressors. However, when cortisol remains elevated for prolonged periods, it can negatively impact our health.
Acute stress is the body’s quick, natural reaction to a perceived threat or challenge. It’s a short-term response triggered by situations like preparing for an important presentation or narrowly avoiding an accident. During acute stress, cortisol levels temporarily increase to help us cope with the immediate demands at hand.
Chronic stress, in contrast, is a long-lasting state of stress that continues over an extended period. It often arises from persistent challenges such as financial struggles, relationship conflicts, or work-related pressures. This ongoing stress results in continuously elevated cortisol levels, which can seriously harm both physical and mental health.
Many of us often experience stress—whether it’s due to an upcoming deadline, challenges with a child’s schooling, or managing multiple responsibilities. However, signs of elevated cortisol go beyond just feeling stressed. Even if you feel momentarily calm, your body might still be under stress, with high levels of stress hormones circulating. Here are some key signs to watch for that may indicate you are experiencing chronic stress.
Persistently high cortisol levels can interfere with normal sleep patterns, causing trouble falling asleep or staying asleep during the night. These disruptions often result in daytime tiredness and impaired mental performance.
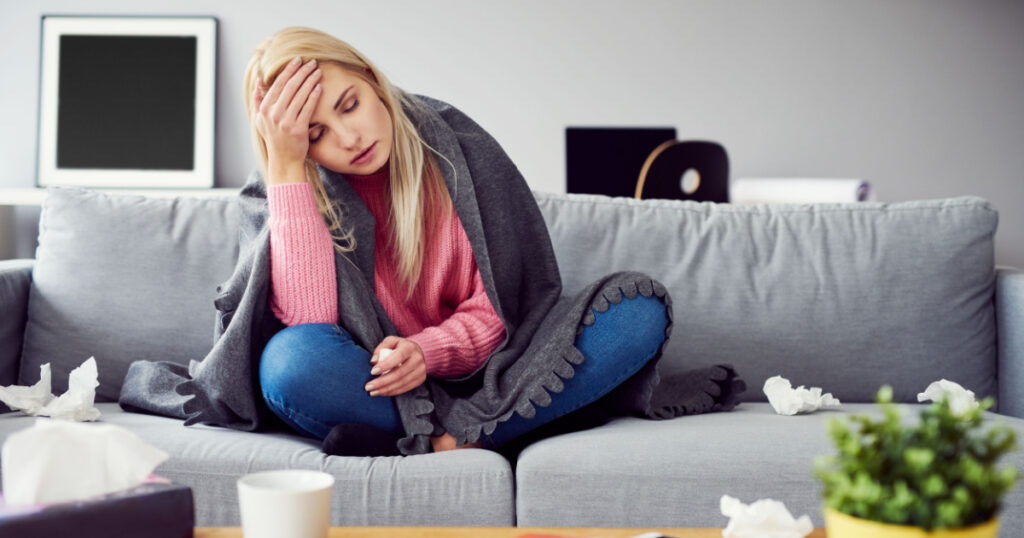

Extended periods of elevated cortisol can weaken the immune system, increasing vulnerability to infections, viruses, and various illnesses. If you notice that you frequently fall ill, it could be a sign that your cortisol levels are elevated.
Elevated cortisol levels can contribute to heightened anxiety and feelings of depression. Cortisol affects brain chemicals like serotonin and dopamine, which play key roles in mood regulation. If you’re experiencing anxiety or depression, it’s important to reach out for professional support—these challenges shouldn’t be faced alone.
Cortisol breaks down muscle tissue, causing muscle weakness and a reduction in muscle mass over time. This can negatively affect physical performance and make it harder to maintain a consistent exercise routine. As a result, many people may feel frustrated when their efforts in the gym don’t seem to produce the desired results.
High cortisol levels can negatively affect memory, concentration, and overall cognitive function. This can lead to difficulty focusing, forgetfulness, and reduced productivity. Similar to low libido, this creates a stressful feedback loop—struggling to focus lowers productivity, which in turn increases stress, perpetuating the cycle.
Chronic stress and elevated cortisol levels have become significant challenges in today’s world, affecting countless people’s health, longevity, and quality of life. Fortunately, there are effective ways to relax and lower cortisol. Here are some helpful strategies:
- Incorporate Relaxation Practices: Make techniques like deep breathing, meditation, or yoga part of your daily routine to better manage stress.
- Prioritize Quality Sleep: Aim for 7 to 8 hours of restful sleep each night to support balanced cortisol levels and overall health.
- Stay Active: Regular physical activity helps reduce stress and boosts endorphin release. Choose enjoyable exercises like walking, jogging, dancing, or swimming, but avoid overdoing it, as excessive exercise can raise stress.
- Eat a Nutritious Diet: Focus on a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains. Limit caffeine, sugary treats, and processed foods. For athletes, ensuring adequate calorie intake is crucial since under-eating can also increase stress.
- Build a Support Network: Surround yourself with caring friends and family who can offer emotional support during stressful times.
- Manage Your Time Wisely: Organize tasks and create schedules to prevent feeling overwhelmed and keep stress in check.
- Engage in Enjoyable Activities: Take time for hobbies and pastimes that relax and uplift you, such as reading, listening to music, taking baths, or spending time outdoors.
- Seek Professional Support When Needed: If stress or cortisol-related symptoms persist or worsen, don’t hesitate to consult a mental health professional for expert advice and assistance.
Identifying the symptoms of elevated cortisol is essential for taking early action to manage stress effectively. By adopting healthy habits and reaching out for support when needed, you can lower cortisol levels and regain control over your health.
Always pay attention to your body’s signals, allow yourself time to rest, and make self-care a priority. With a balanced approach, you can successfully reduce stress and foster a healthier, more harmonious lifestyle.

